Is Budding Asexual Reproduction Full Pack Videos & Photos Free Link
Dive Right In is budding asexual reproduction superior on-demand viewing. Subscription-free on our video archive. Submerge yourself in a wide array of featured videos available in superior quality, suited for first-class watching aficionados. With the freshest picks, you’ll always keep current. Locate is budding asexual reproduction recommended streaming in impressive definition for a utterly absorbing encounter. Hop on board our media world today to experience one-of-a-kind elite content with 100% free, without a subscription. Benefit from continuous additions and venture into a collection of indie creator works produced for deluxe media experts. Don’t miss out on unseen videos—swiftly save now! Access the best of is budding asexual reproduction one-of-a-kind creator videos with vivid imagery and members-only picks.
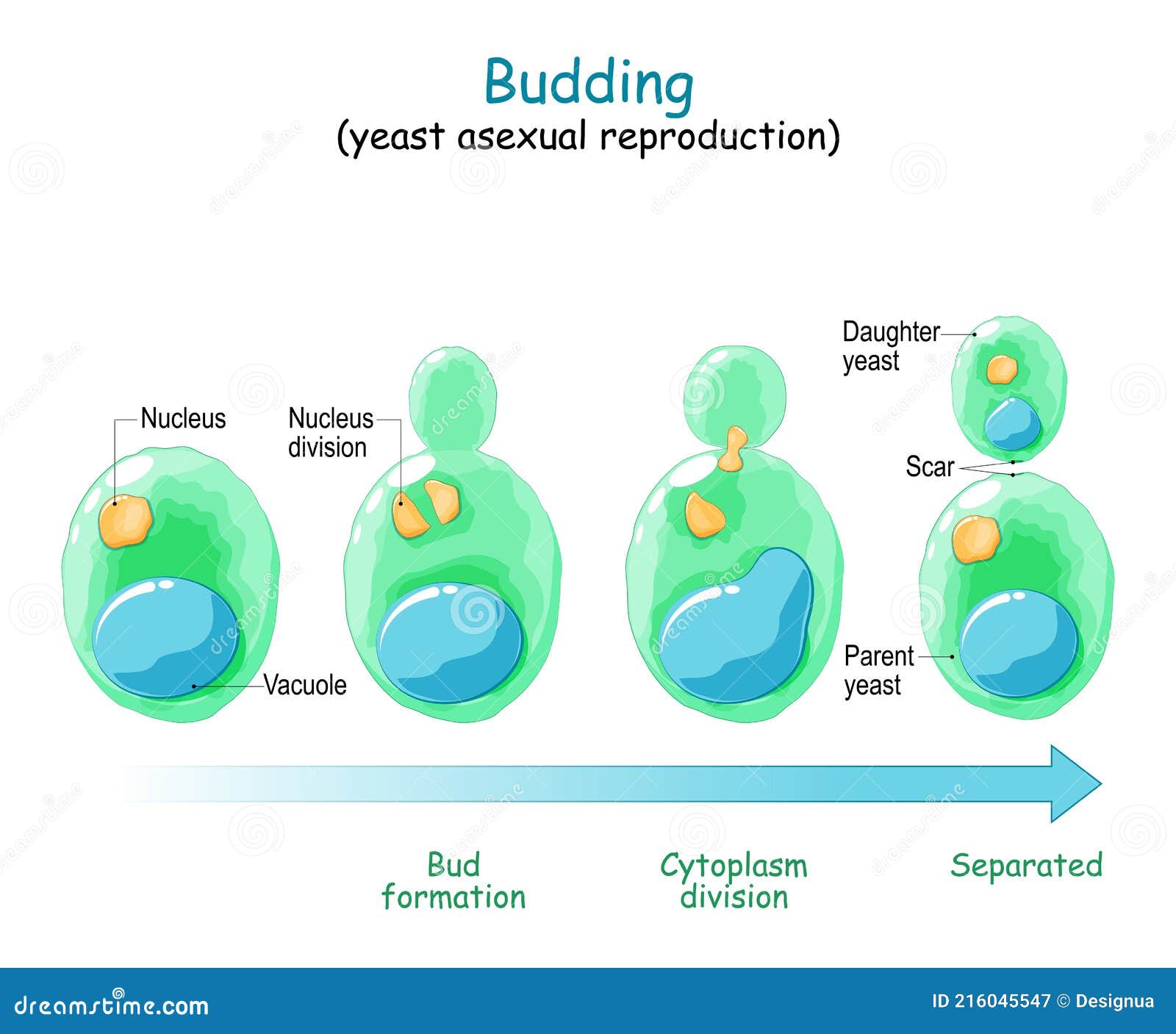
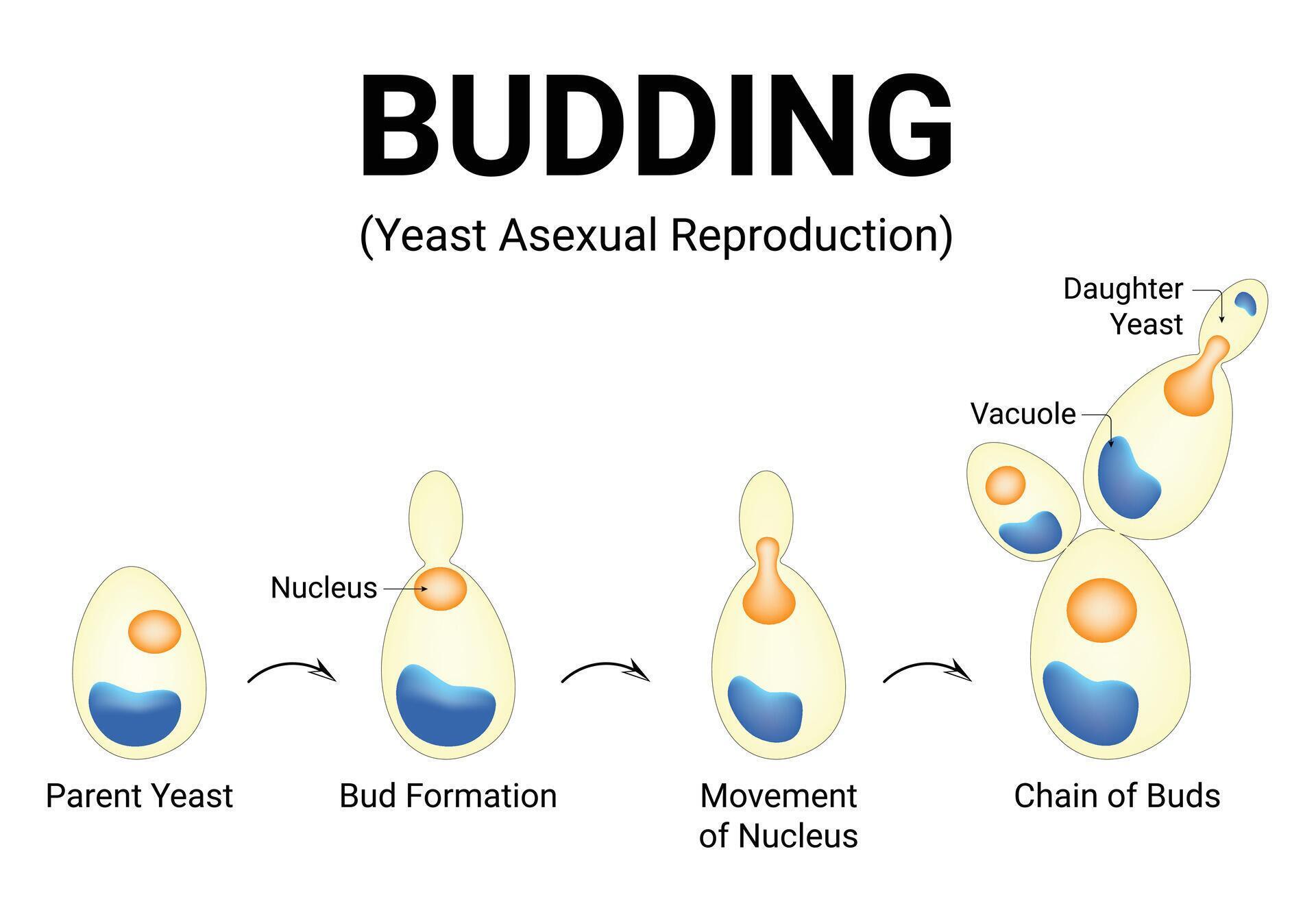
Budding, in biology, a form of asexual reproduction in which a new individual develops from some generative anatomical point of the parent organism Whether in yeast, hydra, or plants, budding allows organisms to quickly and effectively increase their population without the need for genetic recombination. In some species buds may be produced from almost any point of the body, but in many cases budding is restricted to specialized areas.
Budding. Asexual Reproduction of Yeast Cell Stock Vector - Illustration of isolated, science
Budding or blastogenesis is a type of asexual reproduction in which a new organism develops from an outgrowth or bud due to cell division at one particular site. Budding is a fascinating and efficient mode of asexual reproduction that ensures the rapid propagation and survival of species Budding is a mode of asexual reproduction where a new organism develops as an outgrowth from the body of the parent organism
Learn how budding occurs in bacteria, fungi, protozoa, hydra, and plants, and compare it with binary fission.
Definition of budding budding is a type of asexual reproduction Budding is the formation of an individual daughter from a small bud on the parent's body The newly developed progeny produced by this method are genetically and morphologically homologous to the parent organism During budding, a cytoplasmic disruption takes place in the basal area of the parent body and results in the.
Budding is a form of asexual reproduction developing a new individual from the same generative anatomical point of the parent organism restricted to specialized areas However, in some cases, buds can be produced from any point of the body The budding process is observed in various organisms of different species, like fungi, algae, hydra, and some species of coral Asexual reproduction involves producing progeny that are genetic clones of the parent
This can be done by regeneration, budding, and binary fission.